Application
Object Tree
The Application
Object Tree (AOT)
is contains all the objects & code elements in AX.
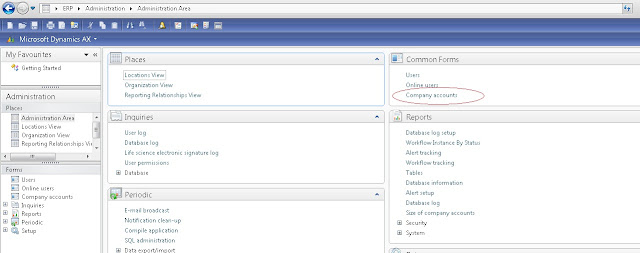
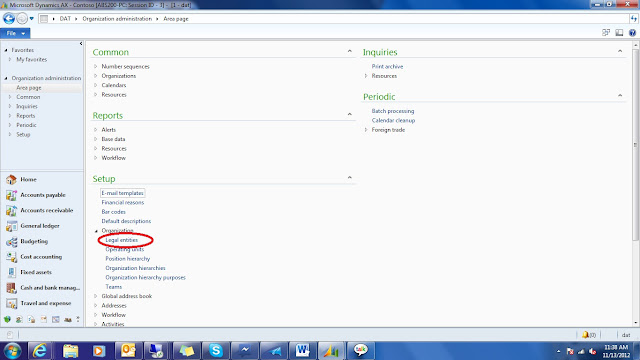
You can open
it by clicking on the icon from the top-menu shown below or by
pressing Ctrl + D from anywhere in AX.
 we can
find the no.of objects in AOT, in the left side of the status bar
we can
find the no.of objects in AOT, in the left side of the status bar
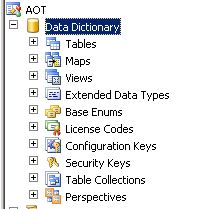
.Data
Dictionary
under the Data Dictionary we can find the following nodes
Under Data
Dictionary node, we will find tables, maps, views, extended
datatypes, base enums, license codes, configuration keys, security keys,
table collections and perspectives.
Macros
Macros are predefined values used
throughout the solution and are present just as a best practice tool. You
won't have to hardcode values into the code, but rather reference a
macro-element within a macro.
Classes
Classes in AX are classes in the
same sense as you are used to from whichever object-oriented programming
language you already know. They are blueprints of how objects should look
at runtime.
Forms
Forms are the end users way of
communicating with the system. They can open forms to search for data,
view data, change data, create new records, or delete records. In
addition, forms very often contain buttons that link to other forms, reports,
and classes that execute business logic.
Data
Sets
The data sets define the tables that
are used by these Visual Studio components by adding the tables to the
data sets much like you would do with table in a data source.
Reports
Reports are the standard AX reports
that will display data in a report form to the users, or write the data to
a printer or file.
Report
Libraries
Report Libraries are links to
reporting projects in Visual Studio. You can't create a reporting library
directly from AX. You have to create a reporting project in Visual Studio
first and import it into AX. It then becomes a report library.
Queries
Queries in the AOT are predefined
static queries that can be reused throughout the whole application. A
query contains a hierarchy of data sources that defines the data that
should be available for the query. Queries can also be used by other elements
in AX such as in forms, reports, and classes.
Jobs
Jobs are static methods intended to
directly execute a small piece of code. They work fine for code that is
supposed to execute once, but are not intended to be a part of a customer
solution.
Menus
Menus present the end user with
options to open the most used forms and reports and to start periodic
tasks.
Menu
Items
 MenuItems are pointers to forms,
reports, or classes. There are three different types of menu items:
Display, Output, and Action. The display menu items are used to open
forms; the output is used to open reports and the action is used to execute
a class with a main method (start point).
MenuItems are pointers to forms,
reports, or classes. There are three different types of menu items:
Display, Output, and Action. The display menu items are used to open
forms; the output is used to open reports and the action is used to execute
a class with a main method (start point).
Web
The Web node consists of subnodes
that in turn hold different types of elements relevant for developing web
applications such as the enterprise portal.
Services
Services are used to set up web
services that let other applications use AX classes through the
Application Integration Framework (AIF). The AIF is used for electronic
communication with trading partners or applications.
Workflow
The workflow framework in AX lets
developers create workflows that define certain execution flows depending
on certain events.
Resources
Resources are files that are
imported into the AX database, and can be referenced in the code from the
resources node in the AOT rather than using a directory and filename on
the disk. These files are typically images, icons, cascaded
stylesheets, and XML files. You can preview the files by selecting a
resources node in the AOT, right-clicking on it, and selecting Open.
System
documentation
At the bottom of the AOT, you can
find different types of help. The system documentation consists of
documentation of the AX core. These are the elements in AX that are not
open source. This means that you, as a developer, have to relate to these
elements as "black-boxes". This means that only you will know what to
put into methods and what you can expect to get back. You can find
information about global functions here such as strlen(). This function
(and most other functions) is documented with an explanation of the input
parameters, return value, and an example of how to use the
function. The same goes for core classes and their methods. Typical core
classes are Map, Array, AsciiIo, FormRun, XppCompiler, and so on, just to
mention a few.
Application
Developer Documentation
Application Developer Documentation
consists of documentation regarding standard AX tables and classes. This
documentation is basically just another way of displaying information that
you, as a developer, should be able to find by browsing the AOT, reading
code, and looking at properties.